All about Transistor
A transistor is a fundamental electronic device that plays a pivotal role in modern technology. Developed in the mid-20th century, transistors revolutionized the field of electronics by replacing bulky and less efficient vacuum tubes. Transistors are integral components in various electronic devices, serving as amplifiers, switches, and signal modulators. In this comprehensive discussion, we will explore the different types of transistors, their working principles, applications, and the impact they have had on technology.
I. Introduction to Transistors
A. Definition and Origin
- A transistor is a semiconductor device that regulates the flow of electrical current. The term "transistor" is derived from its primary functions: "transfer" and "resistor."
- The first practical transistors were developed at Bell Labs in the late 1940s, marking a significant advancement in electronic technology.
B. Importance in Electronics
- Transistors are the building blocks of electronic circuits, enabling the miniaturization of electronic devices and the development of integrated circuits.
- They are used in a myriad of applications, from simple amplifiers in radios to complex digital processors in computers.
II. Types of Transistors
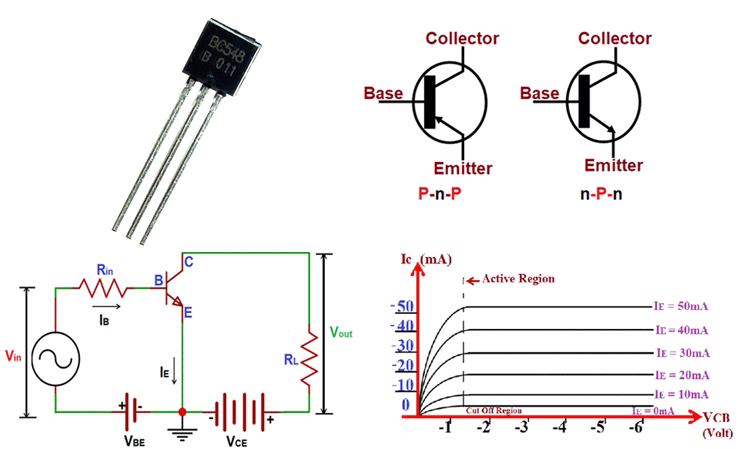
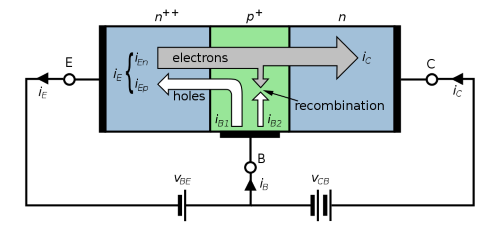
A. Bipolar Junction Transistors (BJTs)
Structure and Operation
- BJTs have three layers of semiconductor material: the emitter, base, and collector.
- The operation involves the flow of charge carriers (electrons or holes) between these layers.
Types of BJTs
- NPN (Negative-Positive-Negative) and PNP (Positive-Negative-Positive) transistors.
- Commonly used in analog circuits for amplification.
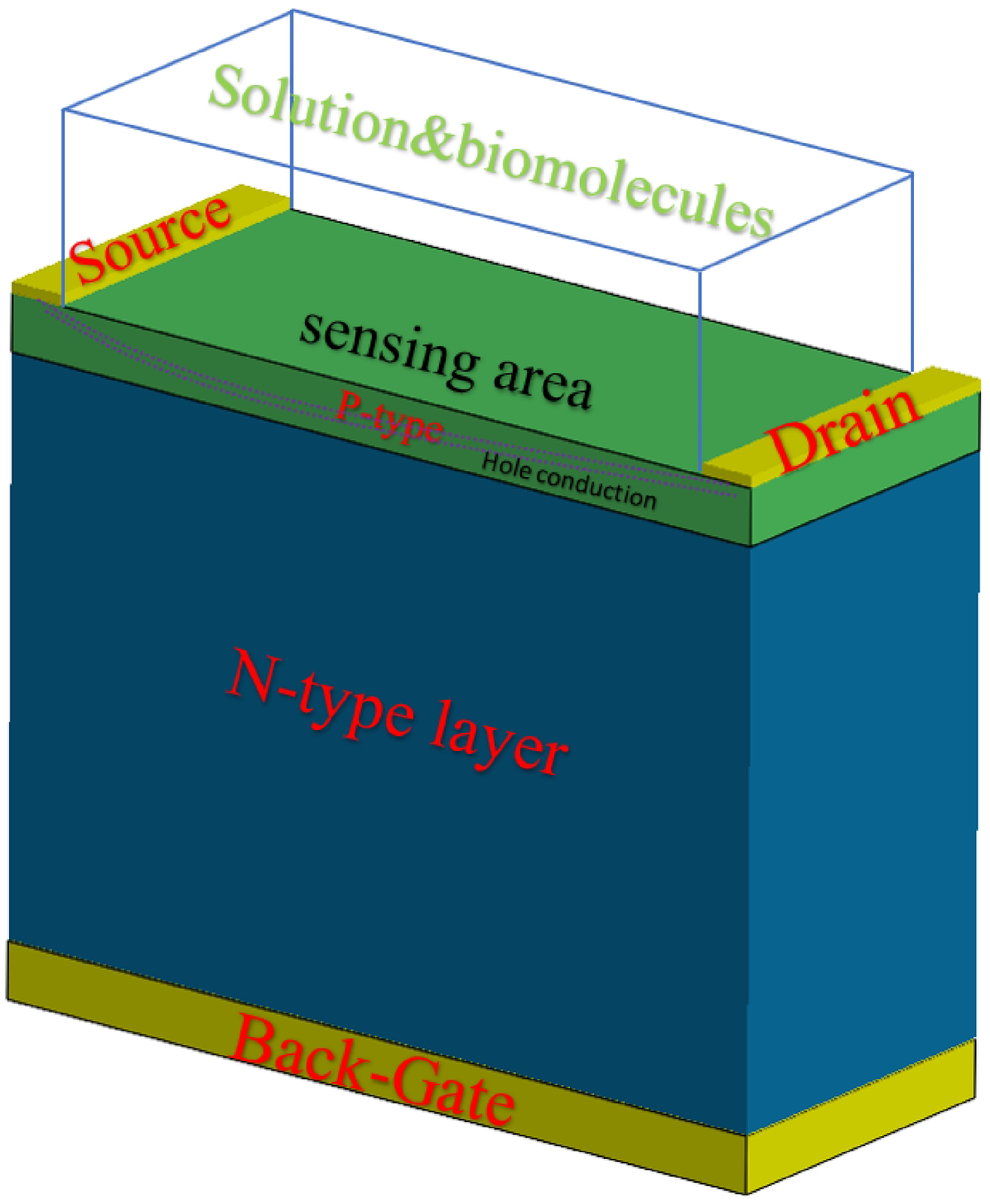
B. Field-Effect Transistors (FETs)
Structure and Operation
- FETs have three terminals: source, gate, and drain.
- The flow of current is controlled by an electric field rather than the movement of charge carriers.
Types of FETs
- Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor FETs (MOSFETs) and Junction FETs (JFETs).
- MOSFETs are widely used in digital circuits.
C. Junction Field-Effect Transistors (JFETs)
- JFETs are characterized by a PN junction between the source and the channel.
- They are voltage-controlled and find applications in amplifiers and switches.
III. Working Principles
A. BJT Operation
Common Emitter Configuration
- Amplification occurs when a small input current controls a larger output current.
Biasing
- Proper biasing is crucial for stable transistor operation.
B. FET Operation
MOSFET Operation
- The gate voltage controls the flow of charge carriers between the source and drain.
JFET Operation
- Voltage applied to the PN junction controls the channel's conductivity.
IV. Applications of Transistors
A. Amplification
- Transistors amplify weak electronic signals, essential in audio amplifiers and communication systems.
B. Switching
- Transistors act as electronic switches, controlling the flow of current in digital circuits.
C. Oscillation
- Transistors contribute to the generation of oscillating signals in electronic devices like radio frequency oscillators.
D. Signal Modulation
- Used in modulation circuits for encoding information onto carrier signals in communication systems.
V. Impact on Technology
A. Miniaturization
- Transistors allowed for the development of compact electronic devices, leading to the miniaturization of technology.
B. Integrated Circuits (ICs)
- The integration of multiple transistors on a single chip paved the way for powerful and complex electronic systems.
C. Advancements in Computing
- Transistors are fundamental to the evolution of computers, contributing to the development of faster and more efficient processors.
VI. Future Trends
A. Nanotechnology
- Continued research in nanotechnology aims to push the limits of transistor miniaturization, enabling even smaller and more powerful devices.
B. Quantum Computing
- Exploring the potential of quantum transistors for the development of quantum computers with unprecedented processing capabilities.
VII. Conclusion
In conclusion, transistors have been instrumental in shaping the landscape of modern electronics. Their various types and applications have paved the way for the development of advanced technologies that impact nearly every aspect of our lives. As we look toward the future, ongoing research and innovations in transistor technology continue to drive progress and open new possibilities in the realm of electronic devices and computing.








Comments