How is Heater work 🤔🤔
A heater operates based on the fundamental principles of heat transfer, typically using electrical energy to generate warmth. The primary mechanisms involved in the functioning of a heater include conduction, convection, and radiation.
Conduction:
One of the fundamental principles behind heating is conduction. In a heater, electricity flows through a conductive material, such as a wire or a heating element. As the electric current passes through this material, it encounters resistance. According to Joule's law, the electric energy is converted into heat energy as a result of this resistance. This process is akin to rubbing your hands together to generate warmth – the friction between your hands produces heat.
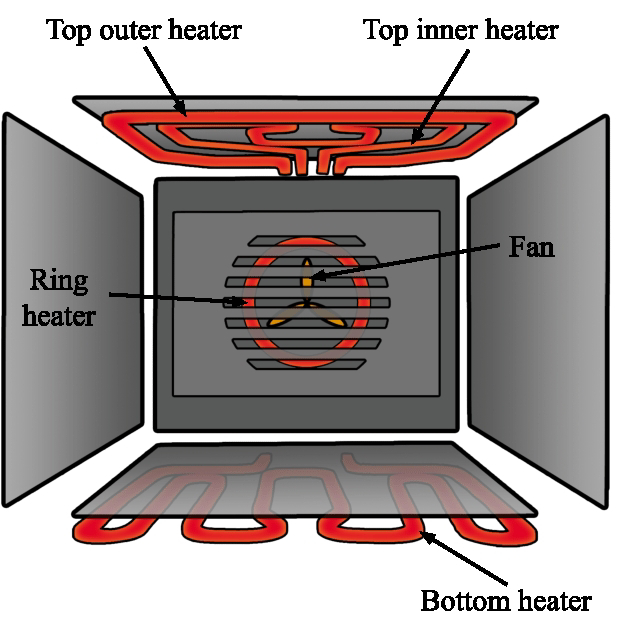
Heating Element:
The heating element is a crucial component in most heaters. It is typically made of materials with high electrical resistance, such as nichrome alloy. When an electric current passes through the heating element, the resistance causes the temperature of the element to rise, leading to the production of heat. This heat is then transferred to the surrounding environment through various means.
Convection:
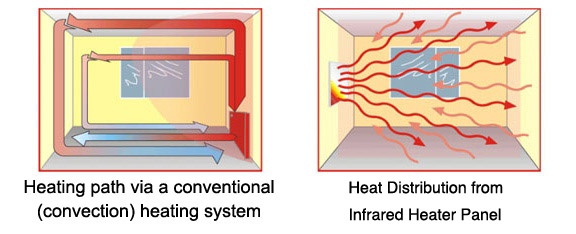
Convection plays a significant role in distributing the generated heat throughout the space. In a heater, convection involves the movement of warm air. As the heating element warms the air in its vicinity, the warm air becomes less dense and rises. This creates a convection current, drawing in cooler air to replace the rising warm air. The continuous cycle of warm air rising and cool air replacing it helps distribute heat evenly in the surrounding area.
Fan-assisted Convection:
Some heaters incorporate a fan to enhance convection. The fan helps in moving air more quickly over the heating element, accelerating the heat transfer process. This type of heater is often more efficient in quickly raising the temperature of a room compared to non-fan heaters.
Radiation:
Radiation is another method by which heat is transferred. In a heater, radiation involves the emission of infrared radiation from the heating element. Infrared radiation is a form of electromagnetic waves that carry heat energy. This heat is then absorbed by objects and surfaces in the room, raising their temperature. This is similar to the way the sun's rays heat the Earth.
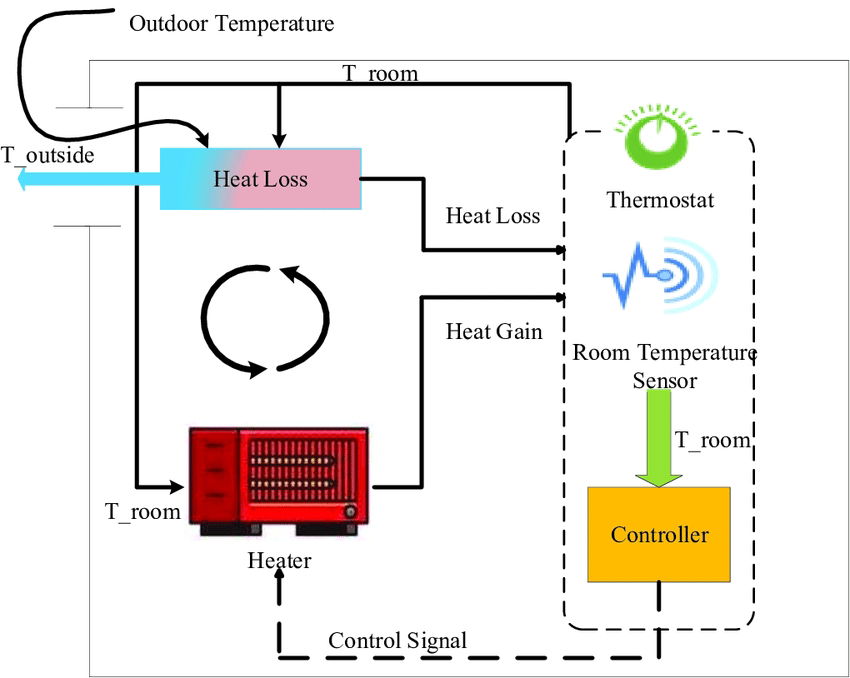
Thermostat and Temperature Control:
To regulate the temperature, heaters are often equipped with thermostats. A thermostat senses the ambient temperature and adjusts the heating output accordingly. When the desired temperature is reached, the thermostat may instruct the heater to reduce or turn off the heating element to maintain the set temperature. This not only provides comfort but also contributes to energy efficiency.
Safety Features:
Modern heaters often include safety features to prevent overheating. These may include automatic shut-off mechanisms that turn off the heater if it reaches a certain temperature. Additionally, some heaters have tip-over switches that cut off power if the unit is accidentally knocked over.
In summary, a heater operates by converting electrical energy into heat energy through the process of resistance in a heating element. Conduction, convection, and radiation work in tandem to distribute the generated heat throughout the space. The integration of a thermostat and safety features enhances the functionality and safety of heaters, making them essential appliances for maintaining comfort in various environments.
For more information visit here









Comments